
In the realm of construction and infrastructure projects, efficient collaboration and data management are critical for success. Building Information Modeling (BIM) has revolutionized the industry by streamlining workflows and improving project accuracy. Among the numerous standards guiding BIM implementation, ISO 19650 stands out as the international benchmark that defines structured information management across the lifecycle of a built asset.
ISO 19650 provides a comprehensive framework for organizing and exchanging information in a digital format, ensuring clarity, efficiency, and interoperability. This guide explores the key aspects of ISO 19650, its role in enhancing BIM workflows, and how organizations can successfully implement this standard.
What is ISO 19650?
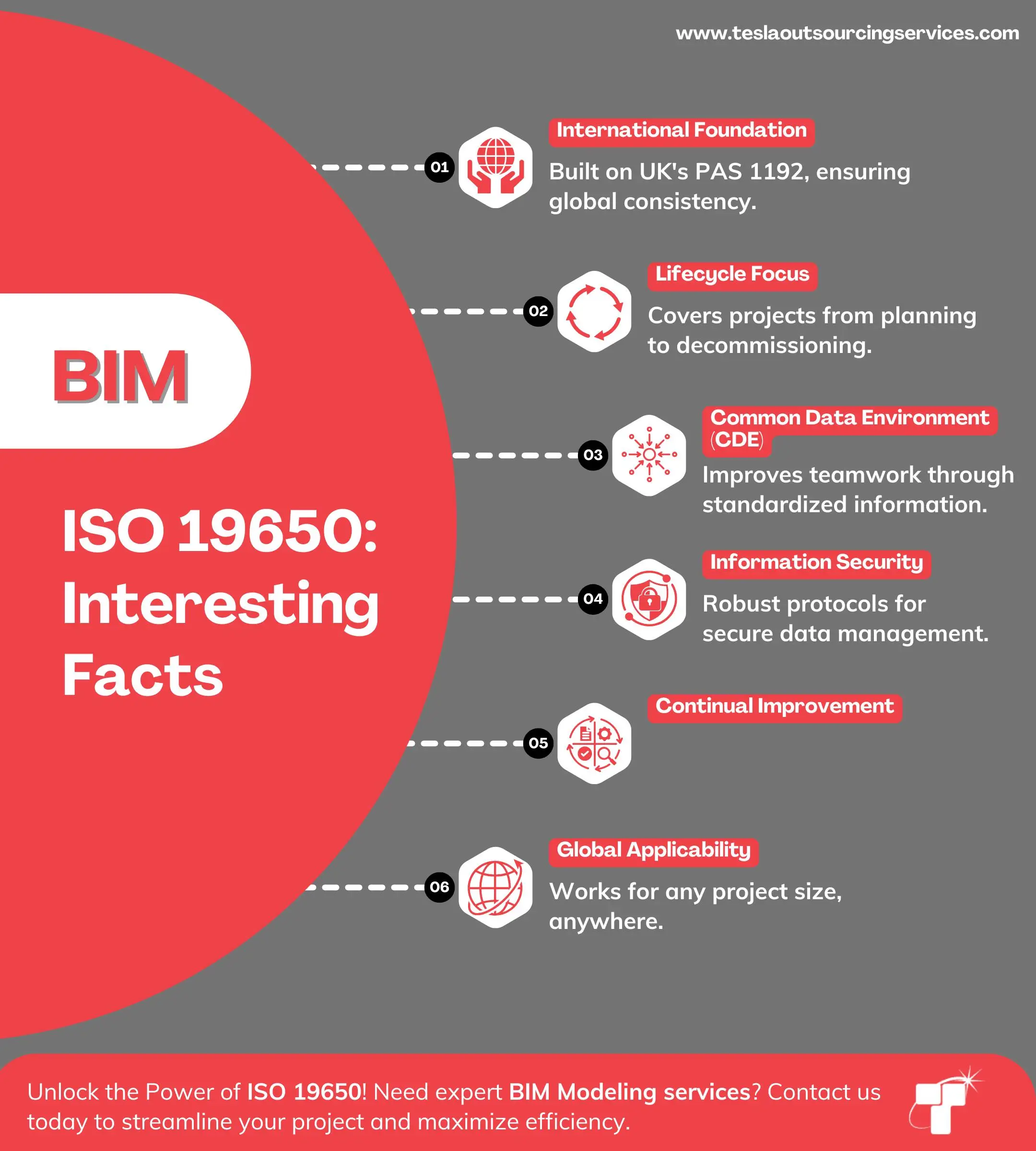
ISO 19650 is an international standard that defines principles and requirements for information management using BIM. It is derived from the UK’s BS 1192 and PAS 1192 series and provides a structured approach for managing information throughout the asset lifecycle.
The standard comprises two primary parts:
- ISO 19650-1: Concepts and Principles - Outlines the fundamental concepts and principles required for effective information management.
- ISO 19650-2: Delivery Phase of Assets - Defines processes for managing information during the design and construction phases.
- ISO 19650-3: Operational Phase of Assets - Focuses on information management after construction.
- ISO 19650-4: Information Exchange - Processes and criteria for the exchange of information between project stakeholders.
- ISO 19650-5: Security-Minded BIM - Addresses security risks associated with digital asset information.
- ISO 19650-6: Health and Safety Information - Supports safety-related data management in BIM environments.
Additional extensions include:
ISO 19650 Decoded!: Unveiling ISO 19650: Interesting Facts and Key Insights into the BIM Standard
Key Principles of ISO 19650
ISO 19650 is based on core principles designed to improve BIM efficiency and project collaboration:
1. Information Management as a Collaborative Effort
- The standard promotes a unified system where stakeholders work together, sharing accurate and structured data to enhance decision-making.
- Establishes roles and responsibilities to avoid data fragmentation and ensure smooth collaboration.
- Encourages transparency, ensuring all parties have access to relevant and verified information.
2. Common Data Environment (CDE)
- The CDE is a digital platform where all project-related information is stored, managed, and exchanged.
- It serves as a single source of truth, reducing miscommunication and information silos.
- Prevents version conflicts, ensuring all stakeholders access up-to-date documents and models.
3. Clear Information Requirements (EIR & PIR)
- Exchange Information Requirements (EIR): Defines the information deliverables expected at different project stages.
- Project Information Requirements (PIR): Specifies the overall data needs throughout the project lifecycle.
- Helps ensure that project teams produce relevant and valuable data aligned with client expectations.
4. Defined Roles and Responsibilities
- Appointing Party - The project owner or client who defines information requirements.
- Lead Appointed Party - The primary contractor responsible for managing the project’s information workflow.
- Task Teams - Contributors such as architects, engineers, and surveyors who generate data and models. Establishing clear roles ensures accountability and a smooth information flow throughout the project.
5. Standardized Workflows and Naming Conventions
- Consistent data structures, naming conventions, and version control improve transparency.
- Enhances efficiency by making it easier to locate, update, and retrieve critical information.
- Prevents confusion, mislabeling, and document duplication.
Benefits of Implementing ISO 19650
Adopting ISO 19650 brings a range of advantages to construction and BIM-based projects:
- Enhanced Collaboration - Standardized workflows ensure that architects, engineers, contractors, and owners work cohesively.
- Improved Data Accuracy - Reduces discrepancies and ensures data integrity throughout the project lifecycle.
- Time and Cost Efficiency - Streamlined data exchange prevents rework and delays, optimizing resources.
- Regulatory Compliance - Helps organizations adhere to international information management standards, ensuring legal and contractual alignment.
- Better Risk Management - Predictive data analysis enables early detection of potential issues, reducing project risks.
- Sustainability and Lifecycle Management - Enables long-term maintenance, refurbishment, and operational efficiency of built assets.
Steps for Effective ISO 19650 Implementation
To successfully implement ISO 19650, organizations must follow a structured approach:
-
Understand the Standard
- Familiarize all stakeholders with ISO 19650’s guidelines, ensuring a uniform understanding across the organization.
- Conduct training sessions and workshops for employees to bridge knowledge gaps.
-
Establish a Common Data Environment (CDE)
- Implement a robust CDE platform to store and manage information efficiently.
- Select the right BIM software and collaboration tools that align with ISO 19650 standards.
-
Define Information Requirements (EIR & PIR)
- Clearly articulate what data is required, who is responsible for its generation, and when it needs to be delivered.
- Create a well-documented information management plan (IMP) to streamline processes.
-
Assign Roles and Responsibilities
- Designate Appointing Parties, Lead Appointed Parties, and Task Teams to oversee data management.
- Ensure responsibilities are well-documented and agreed upon before project initiation.
-
Adopt Standardized Naming and Classification
- Ensure all documents and data entries follow a consistent structure.
- Use industry-standard classifications to maintain consistency across projects.
-
Implement a Review and Approval Workflow
- Establish mechanisms for verifying, approving, and updating information before use.
- Define key approval milestones to maintain quality assurance.
-
Monitor and Improve Processes
- Continuously assess information management practices and refine workflows for better efficiency.
- Conduct periodic audits to identify areas for improvement and update methodologies accordingly.
Challenges in ISO 19650 Implementation
While ISO 19650 offers substantial benefits, organizations may encounter challenges such as:
- Resistance to Change - Employees and stakeholders accustomed to traditional project management may resist new processes.
- High Initial Investment - Implementing BIM software, training, and establishing a CDE require upfront costs.
- Complexity of Compliance - Organizations must ensure compliance with all parts of ISO 19650, which may involve additional documentation and procedural adjustments.
- Interoperability Issues - Different stakeholders may use varying software platforms, requiring integration and compatibility checks.
Future of ISO 19650 and BIM
The adoption of ISO 19650 is expected to grow, with future developments emphasizing:
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning - Automating BIM workflows and predictive analysis for enhanced decision-making.
- Cloud-Based Collaboration - Expanding CDE capabilities for real-time collaboration across global teams.
- Sustainability Initiatives - Leveraging BIM for greener, energy-efficient building practices.
- Government Mandates - More countries adopting ISO 19650 compliance as a regulatory requirement for public infrastructure projects.
Conclusion
ISO 19650 is a crucial standard that helps organizations implement structured BIM practices, ensuring efficient project execution and enhanced collaboration. By following its principles, the construction industry can achieve improved data management, cost savings, and higher-quality outcomes. Organizations looking to integrate BIM must adopt ISO 19650’s methodologies to stay ahead in an increasingly digitalized industry.